This report is a general overview of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)—a physiologic communication system that helps regulate various functions within the human body. The ECS was only discovered in the 1990s, as numerous studies are linking multiple diseases and chronic health conditions to an imbalance of the ECS. For many who suffer from chronic diseases and illnesses related to deficiencies within the ECS, Cannabidiol (CBD) has the potential to provide an alternative natural option for general well-being. While large-scale, double-blind clinical trials on CBD are still lacking, this document is designed to give you a general overview and basic understanding of the ECS in which CBD plays an integral role. This report is based on a good amount of preclinical published data that is available and is supported by the Physicians CBD Council. The mission of the Council is to advocate for medical research for therapeutic opportunities and educate on the potential risk and health benefits of cannabis based on current published data.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a molecular system whose role is to maintain “homeostasis” in the body. This system is present in all vertebrate species and has been around for at least 700 years.
Homeostasis is a concept that most biological systems function best in a narrow range – similar to the Chinese “Yin and Yang” theory of balance. Conditions must be “in the right balance” for our cells to function well and maintain optimal health. When conditions are “out of balance,” we develop chronic diseases.
There are three key components of the ECS:
- Cannabinoid receptors found on the surface of cells
- Endocannabinoids – molecules produced by our body that activate the cannabinoid receptors
- Metabolic enzymes that break down endocannabinoids after they are used
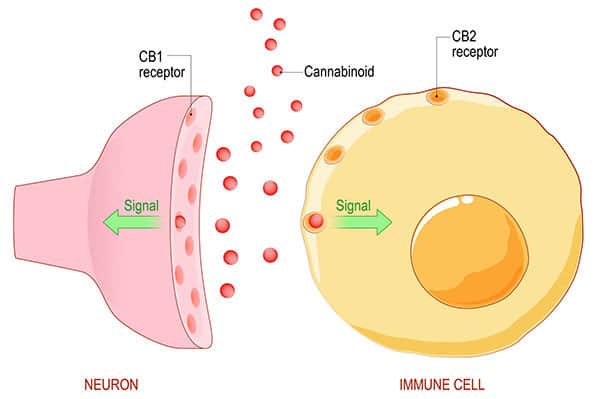
Cannabinoid Receptors
Cannabinoid receptors are located on the surface of cells and “listen” to conditions outside the cell. When the receptors are “activated,” they transmit information about changing conditions outside the cell and trigger appropriate cellular responses. The two primary cannabinoid receptors are CB1 and CB2. CB1 is found primarily in the brain and central nervous system, whereas CB2 receptors are more abundant throughout the body, including immune system cells.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are produced naturally by cells of the human body. They are made “on-demand” and used only when they are needed. They are not made and stored for later use like many other molecules. Two major endocannabinoids are produced by the body- Anandamide and 2-AG. They are known to bind and activate CB1 and CB2 receptors. Once they are used, the metabolic enzymes (the third piece of the endocannabinoid triad) quickly destroy the Endocannabinoids.
Metabolic Enzymes
The enzymes of the endocannabinoid system's role is to break down the endocannabinoids once they are used (bind to receptors). This process occurs quickly to ensure that the endocannabinoids are used when they are needed but not longer than necessary. The two main key enzymes are FAAH (breaks down anandamide) and MAGL (breaks down 2-AG).
The three components of the ECS is found in most organ systems of our bodies. The role of ECS is to maintain homeostasis – when something brings the body out of homeostasis, the ECS is called upon to bring the body back into homeostasis. The ECS system is only engaged when it's needed to bring the body back to homeostasis.
Homeostasis
Homeostasis applies to all physiologic processes in our bodies. If our body's core temperature is too high (“having a fever”), our body's cellular mechanism attempts to bring its core temperature back to a normal range. If our body's core temperature is too low, we develop “shivering” to generate heat and bring our core temperature back to balance. If our blood pressure is too high or too low, or our blood sugar too high or too low, our body has processes designed to bring the system back to balance, “homeostasis.” The endocannabinoid system's role is to detect when our body systems are outside of balance and produces endocannabinoids “just in time” when needed at specific locations required to bring health systems back to homeostasis.

Autophagy
Autophagy is a cellular process designed to maintain homeostasis. The balance between the creation of new cells in our bodies and the self-degradation and disassembly of “old cells” (“Autophagy”) is required for homeostasis and optimal health. Therefore, to maintain optimal health, the “new cell creation” rate needs to be equal to the rate of “old cells removal.”
When this balance is disrupted, disease processes occur. For example, osteoporosis occurs when the rate of removal of “old bone cells” exceeds the creation of new bone cells. Leukemia occurs when the specific creation of new white blood cells exceeds the removal of old white blood cells. In other words, cancer occurs when “cells refuse to die” and develop into a “cancer mass.” Defective autophagy is associated with disease conditions such as cancer, autoimmune disease, neurodegenerative disease, and the process of aging. Activation of ECS plays a regulatory role in the autophagy process to maintain a balance between cell survival and cell destruction.
Endocannabinoid Regulation of Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural protective process the immune system has to defend the body against pathogens (virus, bacteria, infection, etc.) and toxins. The purpose of inflammation is to remove germs and damaged tissue. When the immune system detects a pathogen or toxin it views as threatening, it activates the inflammatory response that triggers fluid accumulation (swelling), increased circulation, and white blood cell “soldiers” to come to remove pathogens and damaged tissue. Inflammation must be limited and temporary – it ends when the threat to the body stops.
When inflammation becomes chronic and long-term, the process damages healthy tissue and organs and creates chronic disease. Chronic inflammation is associated with common conditions affecting all systems of our bodies:
- Chronic inflammation of the lung – Asthma, and COPD
- Chronic inflammation of GI tract – Crohn's disease, Ulcerative Colitis, Celiac disease
- Chronic inflammation of joints – Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis, Gout, Chronic inflammation of kidneys – glomerulonephritis
- Chronic inflammation of the brain – Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Multiple Sclerosis
In general, endocannabinoid studies suggest that ECS suppresses or limits the immune system from producing excessive inflammation. When immune cells release an inflammatory response to fight pathogens, endocannabinoids are also released to help regulate the magnitude and extent of this inflammatory response. This dual system promotes homeostasis, or balance, in the function of our immune system and controls inflammation. In addition, the lack of balance with inflammation leads to pathogenic states and chronic illness.
Plant Cannabinoids (CBD & THC)
The Marijuana plant has over 100 plant cannabinoid compounds. THC and CBD are the most popularly studied cannabinoids. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a compound found in the cannabis plant, and the vast majority is extracted from the hemp plant. Hemp is part of the cannabis Sativa plant with very low levels of THC (defined as having less than 0.3% THC). Unlike THC, CBD is considered “non-psychoactive.” Plant cannabinoids activate directly or indirectly the Endocannabinoid System and numerous other receptor types in the brain and body. CBD modifies other compounds in the system (e.g., increases levels of anandamide). Importantly, activating the ECS internally or externally with plant or synthetic cannabinoids isn't a “cure-all” for diseases. The ECS stimulation can also go awry – cannabis use in a young developing brain can cause long-term negative health consequences.
Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system is believed to help support the human body by promoting homeostasis in body systems, which is done through processes such as regulating autophagy and inflammation. Based on preclinical research, activating the ECS through CBD can help with sleep, mood, immunity, pain, and possibly even the endocrine system. CBD research is just in its infancy, but clinical trials are increasing exponentially to study potential health benefits.
This information is for educational purposes only. Any recommendations therein are not intended to replace the advice of your health care professional; individual results may vary. However, these statements have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.


Physician CBD Certification Course/Kairos University
Learn CBD from the Physicians CBD Council/ Kairos University. You get a Comprehensive tour of the Endocannabinoid system and associated organ systems.