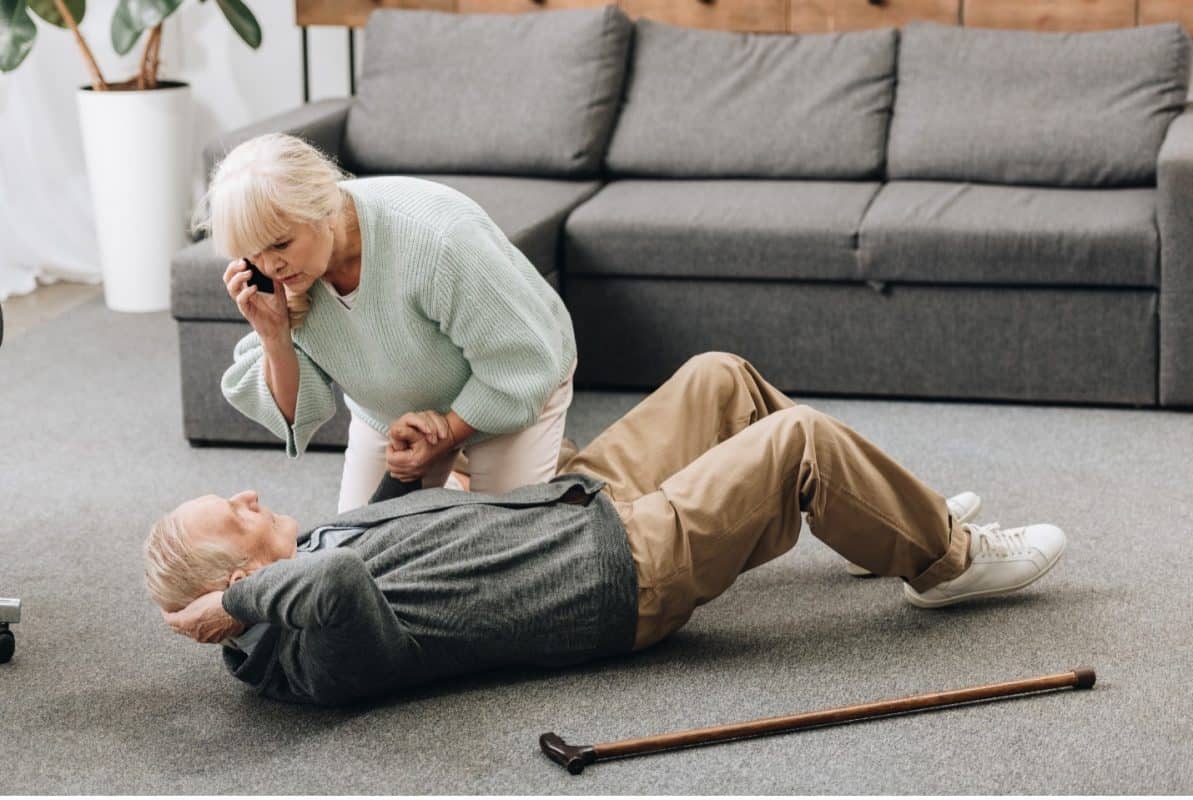
Each year, millions of elderly individuals over 65 will experience a fall, and many will fall again soon after the first fall. These falls often result in serious injuries, such as fractures or head injuries.
In fact, according to the CDC, 800,000 individuals annually over the age of 65 are hospitalized due to a fall. In addition, falls are the second leading cause of unintended fatality worldwide, and they are the leading cause of death in individuals over the age of 65.
The prevalence of falling and its accompanying consequences in the elderly is a significant problem, and the problem is even more exacerbated by unreported falls that go untreated.
In what follows, we’ll discuss the problem with falls in the elderly and the associated causes and complications associated with these falls. We’ll also cover some of the preventative measures to decrease risk.
Common Causes of Elderly Falls
Because we know that the leading cause of elderly deaths, injuries, and hospitalizations is falling, it’s essential to identify the primary causes of these falls.
Some of the common causes of falls in the elderly include:
• General Weakness and Osteoporosis
• Medication Side Effects
• Stroke or Heart Attack
Generalized Weakness and Osteoporosis
As individuals age, they risk falling because older muscles will lose some strength over time. In addition, osteoporosis, which is the condition where bones become more brittle and fragile, often due to calcium or vitamin D deficiency, is a prevalent elderly condition. The combination of these issues will increase the risk of falls dramatically.
Medication Side Effects
Certain medications are a well-documented risk factor for falling. For example, medications used for the treatment of such conditions as high blood pressure and heart disease can cause the side effects of dizziness and fainting. Some individuals can be susceptible to high blood pressure medication, and the medication can cause a significant decrease in resting blood pressure. When this occurs, the risk of becoming dizzy and passing out is relatively high. In addition, certain heart medications can also cause these same side effects.
Stroke or Heart Attack
It’s also possible that an acute medical illness, such as a stroke or a heart attack can lead to falls in the elderly.
Other potential causes for elderly falls can be decreased vision, slow reflexes, or cognitive impairment.
Complications of Elderly Falls
Several complications can occur with elderly falls, and the risks of these complications can be pretty high in the geriatric population.
These are some of the common complications associated with elderly falls:
• Head Injuries
• Hip Fractures
• Bleeding Complications
Head Injuries
Head injuries can occur more commonly in elderly individuals because they are less likely to be able to protect their heads in a fall compared to the younger population. These injuries can be as simple as a bruise or as complicated as a traumatic brain injury.
One of the highest incidences of traumatic brain injury is in the over 85-year age group.

Hip Fractures
The rate of hip fractures in the elderly is rising yearly, and most causes are accidental falls. For example, in 95% of hip fracture cases in individuals over 65, the cause of the fracture is a fall.
Bleeding Complications
If an elderly individual is on blood thinners for a medical condition, the risk of bleeding complications post-fall increases significantly. For example, head injuries that cause lacerations of the scalp in these individuals can be even more severe since the scalp is a highly vascular area.
Preventative Measures for Falls in The Elderly
Because the causes of falls can often be linked to the sedentary lifestyles of the elderly, some of the most effective preventative measures for falls include exercise and physical activity.
Some of the best preventative measures an aging individual should implement to combat the risk of falling include exercise, environmental adjustments, creative interventions, and using specific tools such as walkers and wheelchairs where necessary. In addition, older individuals must understand that their age will require specific adjustments to their behavior, and they need to be willing to accept assistance in certain activities.
In some cases, it might be a good idea to find the senior living cost for special senior living care or communities to help lower the risk of falls or to have help on hand should there be an incident.
Items like walk-in tubs are useful in the bathroom and even in a bedroom close to a water source, this model had a low threshold for entry and many safety features for peace of mind.
When taking blood pressure or heart medication, it’s vital to closely monitor their blood pressure throughout the day to ensure that the medication dosage is correct for them and that their blood pressure does not become too low to walk upright without assistance safely. Using a cane or walker is helpful when taking any new medications to help prevent falls. In addition, health care providers must determine if the risk of falls and injury is higher than the benefits of medication treatment for elderly individuals.
Conclusion
Falls in the elderly population can result in significant complications. These complications can markedly impair an older individual’s quality of life. The utmost attention should be made to preventing falls in the elderly population.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Facts About Falls
- World Health Organization – Falls
- American Family Physician – Falls in the Elderly
- National Library of Medicine – Falls in the elderly



